Consolidated B24
"Liberator"
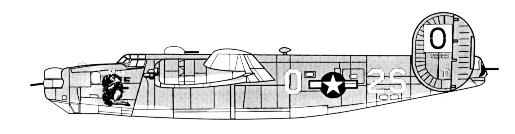
"Aries," 834th BS/486th BG
(source: Academy Model Kit)
The Consolidated B-24 was a follow on design to the Boeing B-17, and was first flown in December of 1939. The B-24 used the Davis wing which was more aerodynamically efficient than the Clark wing used by the B17s. This wing design reduced drag allowing a greater cruising speed and fuel efficiency. The fuselage was taller and more rectangular which increased its internal volume. This translated into a larger payload capacity. Bombs were stowed in two bays each with two racks. The bomb-bay doors rolled up along the fuselage rather than into the slip stream like other bombers. The Liberator had tricycle landing gear and a glassed-in cockpit which improved its visibility for taxi-ing on the runway. The B24 had a crew of 10 men: Nose gunner (G model and later), navigator, bombardier, pilot, copilot, radioman, top gunner/engineer, waist gunner, ball gunner and a tail gunner. The waist gunner would man left and right gun stations. Defensive firepower eventually included 4 twin-gunned turrets; one in the nose, tail, top and belly and two waist gun stations.
Like many other US aircraft the B24 was first employed by the British RAF. The B24 saw use ranging from its intended bombing missions, to use as a ferry aircraft and coastal command aircraft. In the latter version an air to surface radar was installed. The RAF introduced gun turrets in the tail, top and belly positions. The USAAF would add the nose turret in the G model.
Mass production began in 1941 with the "D" model. This version placed the oil cooler to the side of the Pratt&Whitney engines giving the engine nacelles an oval shape. The turbocharger was placed on the underside of the nacelle. This model had a glass nose for the bombardier and had no frontal armament. The E and F variants differed little from the D, but the G sported a new gun turret in the nose. The follow-on variants had only minor changes.
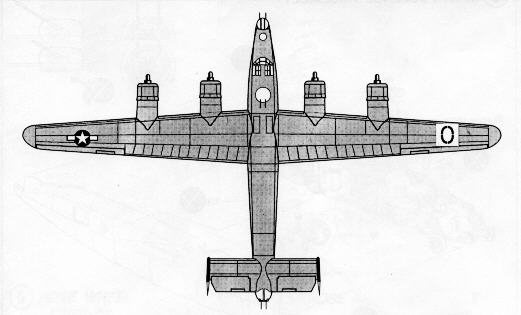
(source: Academy Model Kit)
The B24 was produced in large quantities, surpassing B17 production. Of the 19,203 Liberators built, 6,678 were the "J" version making it the most numerous. The B24 also operated with the USN in the PB4Y-2, "Privateer," version. This aircraft had a single dorsal fin rather than the two fins seen in earlier version. The single fin first appeared in the XB-24K variant. Production of the B24 was carried out at several plants in the US. The Consolidated plant in San Diego was 1 mile long. The production rate peaked at 2 every hour.
B-24 Data:
- WING SPAN: 33.5 m (110ft 0in)
- WING AREA: 97.36 m square (1,048 ft square)
- Length: 20.47 m (67 ft 2in)
- Weight: (J model) 16,738 kg (37,000 lb), maximum 29,484 kg (65,000 lbs).
- Engines: 4 Pratt&Whitney R-1830 Twin Wasp 14 cylinder radials giving 1200 HP.
- Max Speed: (J model) 467 km/h (290mph).
- Service ceiling: 8500 m (28,000 ft).
- Range: 4000 km (2,500 mi) with a bomb load of 2,268 kg (5,000 lbs).
- Armament: 4 twin 50 caliber, 2 single 50 caliber in the waist. Standard bomb load is 8,000lbs.
The B17 "Flying Fortress."
Norden Bombsight
Bomber formation
B24 Restoration at Hill AFB
Collings Foundation "All American"
Comparisons between the B17 and the B24.
Aircraft of the 486th Bomb Group
Copyright © 1998-2026, 486th Bomb Group Association.